Preface
The development of information technology and network shortens the distance between people and makes people increasingly inseparable from the network. PON (Passive Optical Network) technology, mainly composed of OLT, ODN, and ONU, as we all know, tends to mature and has been widely used so far. ONU is usually placed in the user’s home and varies with the diversity of users’ needs. As for the types of ONU, HGU ONU and SFU ONU are always come into our eyes, but few people can tell the difference between them. What exactly are SFU ONU and HGU ONU? You will get the answer in the rest of the article.
1. PON System
From the beginning, there is necessary to learn about PON as the critical part of ONU. PON (Passive Optical Network) is a kind of single-fiber bidirectional optical access network with a point to multipoint (P2MP) structure with a typical tree-type topology. The system composed of OLT (Optical Line Terminal), ONU (Optical Network Unit), and ODN (Optical Distribution Network) which provides a transmission channel, is what we call the PON system.
In the downlink direction (OLT to ONU), the signal sent by OLT reaches each ONUs through ODN. While in the uplink direction (from ONU to OLT), the signal sent by ONU only reaches OLT, not other ONUs. To avoid data conflict and improve network efficiency, the uplink direction adopts TDMA mode and manages the data transmission of each ONU. ODN provides an optical channel between OLT and ONU. The structure of PON is shown in Figure 1.1.
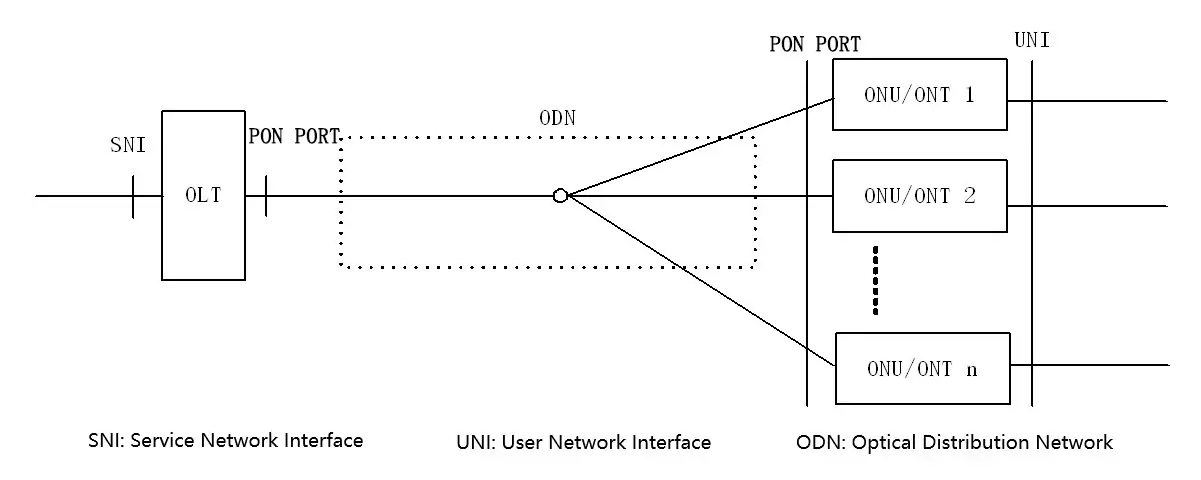
Figure 1.1 PON Structure for Reference
2.What is ONU?
ONU belongs to the terminal equipment of PON technology, playing an essential role in the PON system. ONU, in between the ODN and user equipment, provides the optical interface and the electrical interface to realize the processing, maintenance, and management of various photoelectric signals. There are currently user-side ONU devices, also known as the optical modem, directly installed in home.
The core layer, service layer, and public layer consist of the inner part of ONU. The core layer provides multiplexing and optical interface; the service layer mainly refers to user port, and the public layer ensures power supply and maintenance management. ONU is divided into active optical network units and passive optical network units. Generally, the equipment with an optical receiver, uplink optical transmitter, and multiple bridge amplifiers is called an optical node. The PON connects to the OLT which connects to the ONU through a single fiber. ONU can access various user terminals, such as set-top box, wireless router, TV, etc., and occupies functions of photoelectric conversion, maintenance, and monitoring.
3.Classification and Application of ONU
According to the application, ONU can be divided into six types, namely SFU (Single Family Unit) ONU, HGU (Home Gateway Unit) ONU, MDU (Multi-Dwelling Unit) ONU, SBU (Single Business Unit) ONU, MTU (Multi-Tenant Unit) ONU and CBU (Cellular Backhaul Unit) ONU. However, only SFU (Single Family Unit) ONU and HGU (Home Gateway Unit) ONU are used by the end-users in practical application.
These two types of ONUs will be introduced in the following.
(1)HGU(Home Gateway Unit)ONU
HGU ONU takes the Virtual Ethernet interface point (VEIP) as the partition point of the OMCI management domain and the non OMCI management domain (TR069, SNMP, etc.) in the data plane. The ME achieves management only through OMCI. The non OMCI management domain can only manage all services and functional modules under the VEIP. Only one VEIP is allowed in each HGU. ONU will report VEIP or PPTP (Physical Path Termination Point) when MIB is uploaded according to the type of the device, while HGU can only use and report VEIP rather than PPTP. OLT will judge the type of ONU devices according to the attribution of ONU type in ONU capability. Figure 3.1 shows the service process of HGU ONU.
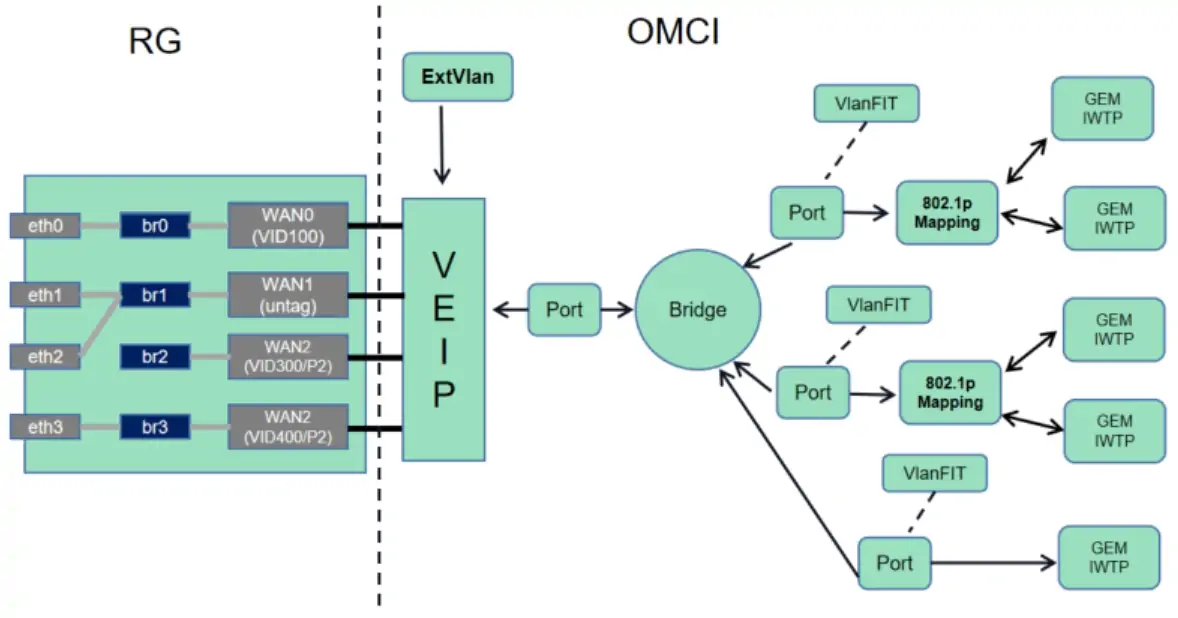
Figure 3.1 Service Process of HGU ONU
HGU ONU, a home gateway with an uplink interface of the PON, is designed for the single family unit, which is similar to SFU ONU. Compared to SFU ONU, HGU ONU integrates the functions of ONU and RG to realize more complex control and management and provide Ethernet / IP service, VoIP service, and optional CATV service. HGU ONU has an Ethernet interface and pots interface, and WLAN interface, USB interface, and CATV RF interface are also available. Besides, TR-069 remote management and EMS local and remote management of physical layer and link layer related to PON interface are supported by HGU ONU that mainly used in FTTH scenarios.
Classified by the differences in service processes and interface numbers of ONUs, HGU ONUs has two specific forms shown in table 3-1.
Table 3-1 Specific Forms of HGU ONU
| Number | Interface Type | Quantity of Ethernet Ports | Quantity of POTS Port | Quantity of WLAN Ports | Quantity of USB Ports | CATV RF Port |
| HGU-1A | 1G | 4 FE | 2(or 1) | 1(or 2) | 1 | optional |
| HGU-1B | 10G/1G | 4 GE or FE | 2(or 1) | 1(or 2) | 1 | optional |
| HGU-2A | 1G | 4(or 2)FE | 2(or 1) | 0 | 0 | optional |
| HGU-2B | 10G/1G | 4(or 2)GE or FE | 2(or 1) | 0 | 0 | optional |
Note:
PPTP is that OLT directly sends VLAN data to each physical interface of ONU, fixing the whole processing process of data flow. VEIP virtualizes the total interface of an ONU. OLT and ONU conduct data docking through VEI. The services under VEIP are managed by ONU through their configuration. In short, PPTP is a LAN port, and VEIP is the virtual WAN port in HGU.
(2)SFU(Single Family Unit)ONU
SFU ONU only supports the OMCI management domain. PPTP is what SFU uses and reports, while VEIP is not available. The processing mode of OMCI configured data flow is different from that of RG flow. For OMCI data flow, there is a one-to-one mapping between the GEM port on the WAN side and the UNI port on the LAN side. All data packets can pass through without MAC address learning or forwarding. Wireless interfaces are not allowed in OMCI. Figure 3.2 shows the service process of SFU ONU.
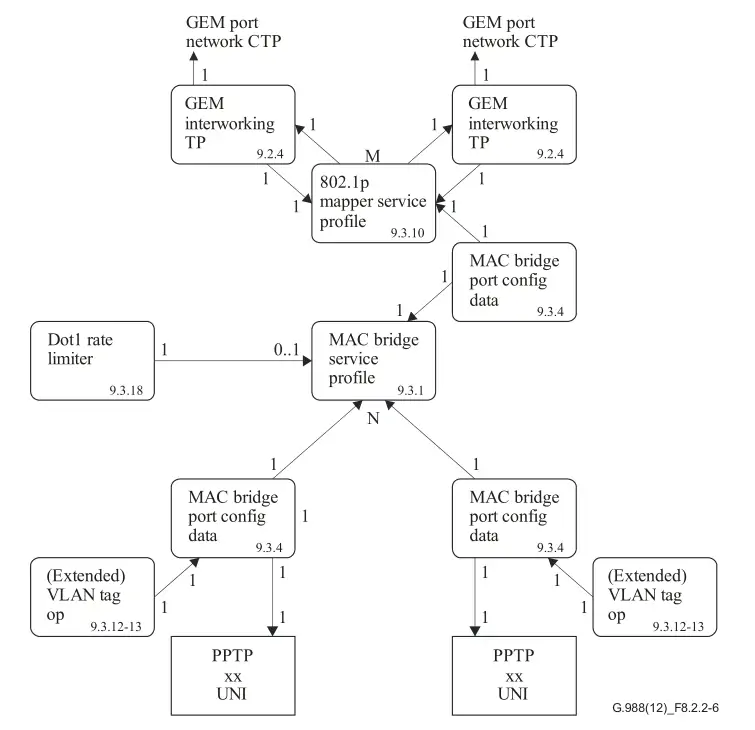
Figure 3.2 Service Process of SFU ONU
SFU ONU is designed for a single family unit with broadband access terminal function without a more complex home gateway function from the perspective of application and ONU capacity. SFU ONU, mainly used in FTTH scenarios, has 1 or 4 Ethernet interfaces and is available for Ethernet / IP services, optional VoIP services (built-in IAD), or CATV services.
There are three specific forms of SFU ONU according to the difference of service process and interface quantity of ONU shown in Table 3-2.
Table 3-2 Specific Forms of SFU ONU
Number | Interface type | Quantity of Ethernet Ports | Quantity of POTS Ports | CATV RF Port |
| SFU-1A | 1G | 1 GE or FE | 0 | optional |
| SFU-1B | 10G/1G | 1 GE or FE | 0 | optional |
| SFU-2A | 1G | 4 FE | 0 | optional |
| SFU-2B | 10G/1G | 4 GE or FE | 0 | optional |
| SFU-3 | 1G | 4 FE | 2 | optional |
Note: SFU is suitable for commercial customers if TDM service is not included.
SFU ONU works under the bridging mode (layer 2 of ISO model), supports multiple VLAN functions, and its Ethernet port can be configured and managed by OLT through OMCI / OAM. Combined with a home gateway, SFU ONU is good at providing strong service capability. However, SFU ONU does not have a three-layer routing function and WAN connection configuration. The Single port 1GE ONU of C-Data is an exception as it has three-layer routing, static routing, PPPoE, DHCP function, etc.
(3)Functional Differences between HGU ONU and SFU ONU
| SFU ONU | HGU ONU | |
| Type of PON | EPON / GPON | EPON / GPON |
| EPON/GPON Standard | IEEE 802.3/802.3ah ITU-TG.984.x | IEEE 802.3/802.3ah ITU-TG.984.x |
| Bridging /Routing | Bridging/L2 | Bridging/L2 and Routing/L3 |
| WAN Configuration | Not support | Support |
| TR069 Function | Not support | Support |
| OLT to configure its Ethernet Ports | Support | Not support |
| NAT Function | Not support | Support |
| Port Forwarding Function | Not support | Support |
| Loop Detection Function | Support | Not support |
| DHCP Server | Not support | Support |
| Wireless WIFI | Not support | Support |
4. C-DATA SFU/HGU ONU
| Number | ONU Form | ONU Model | SFU/HGU |
| 1 | EPON & GPON & XPON 1GE / 1GE + CATV | FD511G & FD701G series | SFU ONU(with routing function) |
| 2 | EPON & GPON & XPON 1GE + Wi-Fi / 1GE + 1FE + Wi-Fi / 4GE + 2 pots + Wi-Fi (AC) | FD511GW & FD512XW & FD702XW & FD604GW & FD804GW series | HGU ONU |
| 3 | EPON & GPON & XPON 1GE + 3FE / 1GE + 3FE + CATV / 4GE | FD50X & FD704X & FD504G series | SFU ONU (without routing function) |
5.Conclusion
Both SFU ONU and HGU ONU have their advantages and disadvantages. The truth is that the main role of ONU is to provide end-users with bandwidth access, playing a vital role in the “last mile” of the access network so that end users can better enjoy the network. Therefore, choosing the right ONU should depend on your network environment.
As a professional ONU supplier, C-Data Shenzhen will focus more on the accumulation and research of technical knowledge to improve our ONU products and meet the customers’ needs for unimpeded network experience. Moreover, C-Data Shenzhen will step further with our customers by improving the quality of products and services without delay.