PON (Passive Optical Network) refers to a fiber optic network that uses point-to-multipoint topology and optical splitters to transmit data from a single point of transmission to multiple user endpoints. Unlike AON (Active Optical Network), where multiple customers connect to a single transceiver via optical branching trees and active splitters/couplers, PON operates entirely in the optical domain and does not require power sources in its architecture. Currently, there are two main PON standards: Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) and Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON).
PON Structure and Components
In an EPON (GEPON) system, the service provider central office houses an Optical Line Terminal (OLT), and there are a certain number of Optical Network Units (ONUs) or Optical Network Terminals (ONTs) near end-users, along with a splitter (optical coupler). Furthermore, an Optical Distribution Network (ODN) is used in the transmission process between the OLT and ONU/ONT.
Optical Line Terminal (OLT)
OLT stands for Optical Line Terminal, which is a device used for connecting fiber optics and transmitting signals. The OLT serves as the starting point of the PON, connected to aggregation switches via Ethernet cables, marking a significant distinction in PON architecture.
Components of OLT Equipment
Generally, OLT equipment includes a chassis, Control and Switching Module (CSM), EPON Link Module (ELM), redundant protection -48V DC power modules or one 110/220V AC power module, fans, and more. Among these components, PON cards and power modules support hot-swapping and include another module internally. OLT operates in two directions: upstream (allocating different types of data and voice traffic from users) and downstream (retrieving data, voice, and video traffic from metropolitan or long-distance networks and sending them to all ONT modules) on the ODN.
Functions of OLT
The OLT device is a crucial central office equipment in EPON. It serves as a multi-service provisioning platform, supporting both IP and traditional TDM services. Placed at the edge of metropolitan networks or community access network exits, it aggregates access services and delivers them separately to IP networks.
Applications of OLT
The OLT device, combined with different types of ONUs, facilitates various access networks such as FTTC, FTTH, FTTO, FTTM, and more. On one hand, the signals carrying different services are aggregated at the central office and sent to end-users, dividing the access network based on specific signal formats. On the other hand, signals from end-users are sent to different service networks based on their business types.
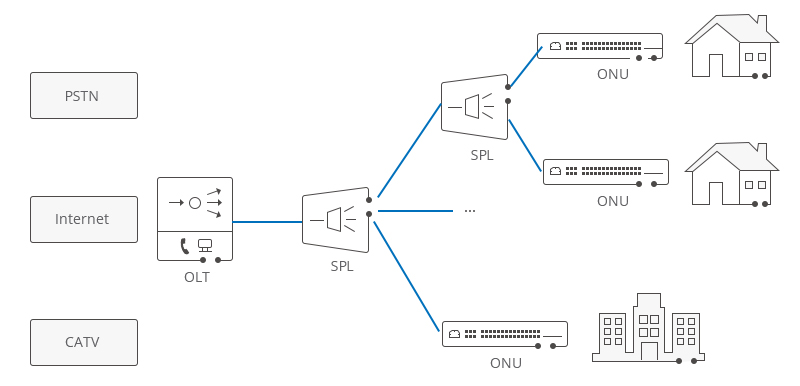
Optical Network Unit (ONU) / Optical Network Terminal (ONT)
ONUs convert optical signals transmitted through fiber optics into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then sent to individual subscribers. Typically, there is a distance or other access network between the ONU and the end-user premises. Furthermore, ONUs can send, aggregate, and groom various types of data from customers and transmit them upstream to the OLT. Grooming is the process of optimizing and reorganizing data streams for more efficient data delivery. OLT supports bandwidth allocation, allowing data to be smoothly sent to the OLT, usually in a bursty manner from customers. ONUs can be connected through various methods and cable types, such as twisted-pair copper, coaxial cable, fiber optics, or Wi-Fi. The end-user devices are also referred to as Optical Network Terminals (ONTs). Essentially, ONT and ONU are the same, ONT being the ITU-T term and ONU being the IEEE term. They both refer to user-side devices in the EPON system but have slight differences in practice based on their locations.
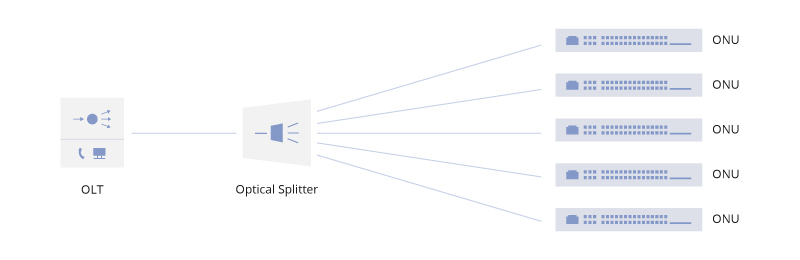
OLT, ONU, and ONT are the main components of a GEPON system, widely used in FTTH applications. Reduced cabling infrastructure (without active components) and flexible media transmission make passive optical networks suitable for home internet, voice, and video applications. Additionally, passive optical networks find applications in university campuses and commercial environments, offering cost-effective solutions. As PON technology continues to evolve, the potential application areas continue to expand.
Choose C-Data for GEPON solutions that prioritize excellence, optimizing your network for seamless and efficient operations. Trust in the quality of C-Data for a superior GEPON experience.