The rapid development of the Internet had brought a large number of intelligent terminals to our home and increasingly exhausted the IPv4 address resources we are using. Although NAT technology helps to delay the speed of the IPv4 address consumption, the world Internet technology is still developing towards IPv6 technology which has become one of the key basic technologies required by 5G, cloud computing and Internet of things technologies.
In the past two years, the world has advocated and accelerated the deployment of IPv6 technology to meet the urgent needs of the connection of massive intelligent terminals, the innovation of technology industries, and the enhancement of network security capability. Almost all ISP/Operators are building the next generation of the Internet based on IPv6 technology.
C-Data, as a professional manufacturer in access network technology, will discuss the following related topics to help you understand IPv6 technology more comprehensively.
Overview of IPv6 Technology
Transition Technology from IPv4 to IPv6
Relevanceof C-Data ONU to IPv6 Technology
C-Data ONU products supporting IPv6 technology
Expectation of IPv6 Technology in The Future
IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6) is the next generation of the current Internet Protocol (IPv4). Composed of 128-bit binary numbers, IPv6 provides a huge resource of IP address enough for every living creature and even every grain of sand on the earth to be assigned one or more IP addresses. IPv6 is to divide the 128-bit address into segments per 16 bits, and each segment is separated by colons when converted into hexadecimal digits.
An example of IPv4 address: 192.168.101.1
An example of IPv6 address: 2002:0db8:85a3:08d3:1319:8a2e: 0370:7344
IPv4 technology is a 32-bit binary address, which can address 16 million networks and 4 billion hosts. However, with the adoption of A, B, and C addressing methods, the number of available network addresses and host machines is greatly reduced. Moreover, as the core technology and about 3 / 4 IP resources are mastered by European and American countries due to their developed Internet, many developing countries fall into the predicament of insufficient IP address resources. In fact, with the increasing number of global Internet users and the vigorous development of intelligent terminals and network technology, the lack of IP address resources will seriously restrict the application and development of the Internet in many countries around the world.
If to realize the complete transition from IPv4 to IPv6, it requires the network software, hardware, and terminal equipment in the global Internet infrastructure to support IPv6 protocol, which will involve a lot of transformation work. Although IPv6 technology has been proposed as early as the 2010 year, it has only been promoted by governments and major ISP/Operators in recent two years. Moreover, the long-term coexistence of IPv4 and IPv6 is still a compatibility issue that we need to consider.
Compared with IPv4, IPv6 has the following advantages:
Larger address space. The IP address length of IPv4 is 32; that is, there are 2^32-1 addresses. While the IP address length of IPv6 is 128, that is, there are 2^128-1 addresses.
Smaller routing table. Compared with IPv4, IPv6 packet header contains half of the fields, and all fields are aligned with 64-bit boundaries, which greatly improves the processing speed.
Enhanced multicast support and streaming support. There is no terrible broadcast storm caused by the IPv4 as the multicast support, and streaming support provide a good opportunity for the development of multimedia services.
Higher security. Users can encrypt the data in the network layer and verify the IP message while using IPv6, which greatly enhances network security.
In view of the advantages of IPv6, IPv6 will eventually completely replace IPv4 and occupy a dominant position on the Internet after a long period of coexistence of IPv4 and IPv6.
Since IPv6 will eventually replace IPv4, how to achieve a network environment fully IPv6 compatible? The initial network transformation from IPv4 to IPv6 reveals that there is a thorough adjustment from protocol to hardware, including the client and server. Therefore, the issue of backward compatibility has been taken into account by IETF when designing IPv6 from the very beginning. The ISP/Operator will provide an intermediate node and uses DNS64 / NAT64 technologies, which are responsible for protocol conversion to connect the link between IPv6 and IPv4.
At the tunnel entrance between the IPv6 and the IPv4, the router encapsulates the entire IPv6 datagram into the data field of the IPv4 datagram. The source address and destination address of the IPv4 packet are respectively the tunnel entrance and exit of IPv4 addresses. At the exit of the tunnel, the IPv6 packet is taken out and forwarded to the destination node.
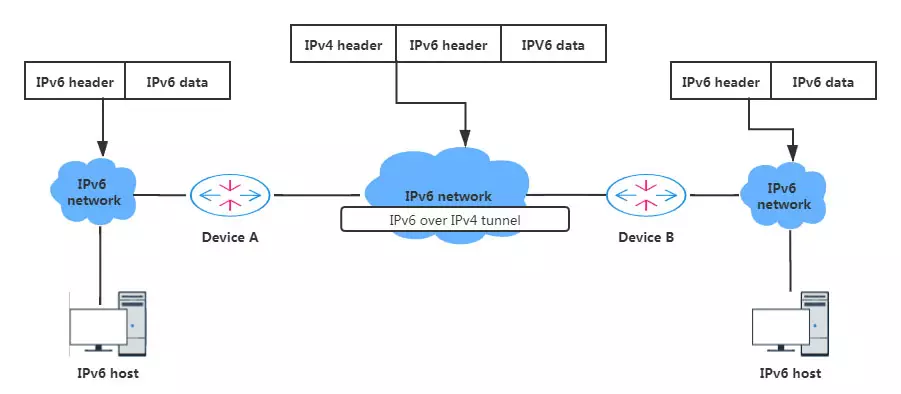
Dual-stack technology is an effective technology for the transition from IPv4 to IPv6. The nodes in the network support both IPv4 and IPv6 protocol stacks. The source node selects different protocol stacks according to the different destination nodes while networking equipment according to the protocol type of the message. A dual-stack can be implemented on a single device or a dual-stack backbone. For a dual-stack backbone network, all devices must support IPv4 / IPv6 protocol stack at the same time, and the interface connecting the dual-stack network must be configured with both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
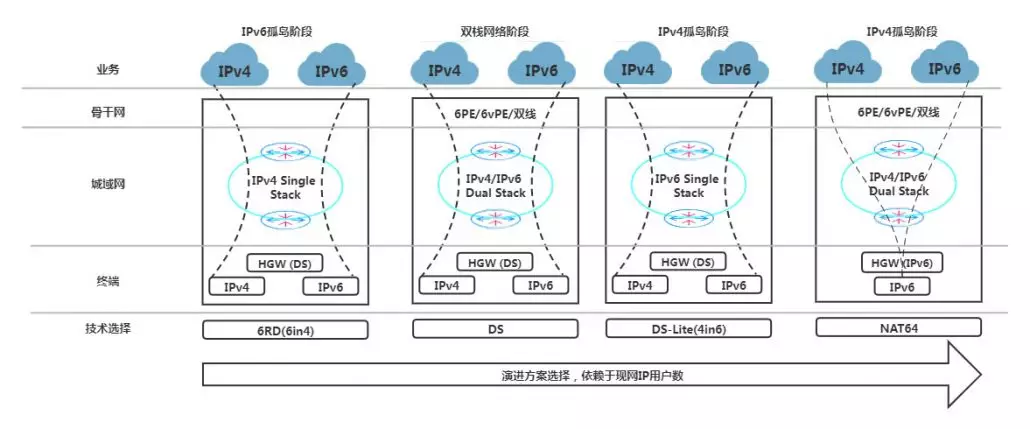
The IPv6 network is divided into a backbone network and an access network. As the backbone network carries a lot of IPv6 services, most ISP/Operators have completed the deployment of the IPv6 backbone network but the access network is used for the access of terminal users. Nowadays, given that almost every family is connected with optical fiber, how to integrate IPv6 function on PON products to solve the problem of IPv6 compatibility is a difficult problem faced by many a ONU manufacturer.
In order to realize fast and easy access to IPv6 network in FTTH and adapt to the needs of global IPv6 network development, C-Data has spared no effort to make ONU support IPv6 service, and a graphical interface is released for end-users to use IPv6 on C-Data ONU easily. Furthermore, C-Data ONU supports IPv4 / IPv6 dual-stack transition technology and has revived the Anatel certification to meet the IPv6 networks in most of the countries. Some countries’ networks have used C-Data ONU as IPv6 network access.
There are two IPv6 network scenarios of C-Data ONU discussing as follows:
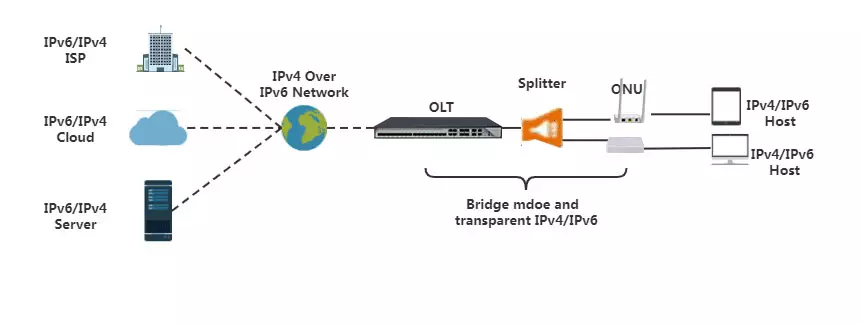
Scenario 1: transparent transmission of IPv4 / IPv6 services by ONU bridge mode
This scenario is mainly used for PPPoE or IPoE of IPv4 / IPv6, with user computers attached to ONU devices or wireless routers attached to ONU devices. Both OLT and ONU during transmission act as middle transmission devices, and only bridge mode is configured to transparently transmit IPv4 / IPv6 services. It is worth noting that whether the intermediate OLT and ONU devices support transparent IPv6 services needs to be considered because there are many OLT and ONU devices on the market that do not support transparent transmission of IPv6 services.
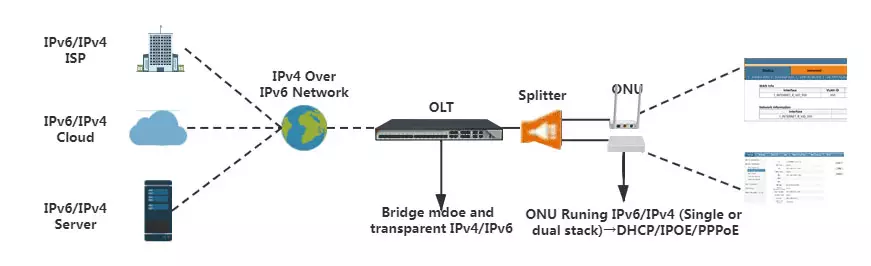
Scenario 2: ONU routing mode carries IPv4 / IPv6 services
In this scenario, the routing mode on ONU should support PPPoE or IPoE services of IPv4 / IPv6, and then allocates IPv4 / IPv6 address to the attached user computer or wireless router through DHCPV4 / DHCPv6 to realize the network access of IPv4 / IPv6. It is available for the OLT devices and the transparent transmission of IPv4 / IPv6. In this scenario, many manufacturers’ ONU products are difficult to implement. However, a lot of ONU manufacturers fail to apply their products to this scenario as there is a couple of issues to figure out, such as the compatibility of IPv6, the implementation of IPv6 Routing, the coexistence of IPv4 and IPv6, and the distribution of IPv6 address.
| No. | ONU Form | ONU Models | Function Description |
| 1 | EPON&GPON&XPON 1GE/1GE+CATV | FD511G&FD701G Series | 1. Support PPPoE / IPoE, DHCPv6, IPv4 / IPv6 dual stack functions of IPv4 and IPv6 in routing mode; 2. Support transparent transmission of IPv4 / IPv6 service in bridge mode. |
| 2 | EPON&GPON&XPON 1GE+wifi/1GE+1FE+wifi/ 4GE+2pots+wifi(AC) | FD511GW&FD512XW&FD702XW&FD604GW&FD804GW Series | 1. Support PPPoE / IPoE, DHCPv6, IPv4 / IPv6 dual stack functions of IPv4 and IPv6 in routing mode; 2. Support transparent transmission of IPv4 / IPv6 service in bridge mode. |
| 3 | EPON&GPON&XPON 1GE+3FE/1GE+3FE+CATV/4GE | FD50X&FD704X&FD504G Series | 1. Only transparent transmission of IPv4 / IPv6 service in bridge mode. |
The global network will build new information technology facilities based on IPv6 and give priority to the use of IPv6 in 5G, the Internet of things, and the industrial Internet.
Technical standards such as IPv6 + and SRv6 will be derived from IPv6 single stack. The application mode will be innovated to increase the pilot and commercial applications under the coordination with industrial chains.
Intelligent ultra-wide, intelligent connection and intelligent operation and maintenance are the main characteristics of the future IP network. IPv6 is the best choice for an intelligent IP network.
AI, big data, cloud computing, and the Internet of things technologies have an important connection with TCP / IP protocol. IP is the network layer protocol standardizing the exchange and routing of Internet packet information. As an infrastructure, IPv6 will construct a new Internet era.
As a professional FTTH broadband access product supplier, C-Data will accelerate the deployment of the IPv6 network together with the global ISP/Operators and apply more IPv6 technologies to the products. If you are interested in IPv6 technology, C-Data welcomes the chance to provide C-Data ONU for you and discuss IPv6 technology together.