With the increase of PON networks’ services, it is necessary to implement PON protection switching technology to ensure the stability of engineering applications stability and deal with service interruptions caused by various communication failures. This article mainly introduces several different PON protection technologies on OLT and describes some implementation points based on a dual PON port protection solution. The ONU remains online, and services are not interrupted before and after the solution is switched. And the delay is less than 100 ms, which greatly guarantees network stability.
PON (Passive Optical Network) is an optical fiber broadband access technology covering the last mile. It only needs to install a simple optical splitter at the optical branch point, which has the advantages of saving optical cable resources, bandwidth resource sharing, no electromagnetic interference, equipment safety, high performance, and low-cost comprehensive network construction. Among them, saving the backbone fiber is a huge advantage of the PON system, but it also brings greater risk. Once the backbone fiber in the PON system fails, it will cause all-optical network units (ONUs) connected to the backbone fiber interrupted simultaneously.
Besides, the system also has the probability of the optical module’s failure and the failure of the port, which is connected to the main fiber. To ensure the service’s stability in engineering applications and deal with the service interruption caused by various communication failures, an efficient and reliable protection switching solution is required. When the backbone fiber fails, the protection switching can be realized in the shortest possible time and recover the services without affecting users’ use.
1.1 PON ProtectionOverview
At present, the commonly used PON protection technologies are the four protection types A, B, C, and D defined in the ITU-TG.984 standards. The protection range of types A and B is the protection from the PON port of the OLT to the optical splitter. The difference between the two is whether the OLT’s PON port is included in the protection range. The protection scope of types C and D is comprehensive protection from the PON port of the OLT to the PON port of the ONU. The difference between the two is whether the ONU’s PON port is included in the protection scope.
1.2 PON Protection Type A
PON protection type A mainly uses a single PON port for the OLT, which has a built-in 1×2 optical switch for the optical module’s gating and then switches the working line. In the optical distribution network (ODN), a 2: N optical splitter is used, and two relatively independent and mutually backup optical fiber links are established between the optical splitter and the OLT. The OLT will detect the line status periodically. When the optical link fails, it switches to the backup optical link.
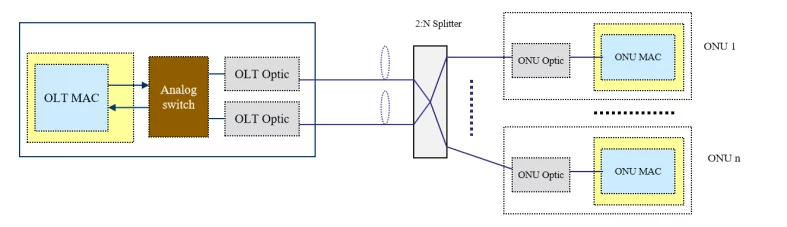
1.3 PON Protection Type B
The OLT’s two PON ports in the PON protection type B adopt independent PON MAC chips and optical modules and are identified as the main PON port and the backup PON port. The main PON port is in a working state, and the standby PON port is in a cold backup state.
In ODN’s optical splitter use, two relatively independent and mutually backup optical fiber links are simultaneously connected between the optical splitter and the OLT. The OLT ensures that the main PON port’s business information can be backed up synchronously and periodically inspect line status and PON port operating status. When the main fiber link or PON port fails, the OLT immediately switches to the backup PON port and fiber link. The backup PON port can maintain the ONU’s service attributes unchanged, and the service is transferred to the backup link.
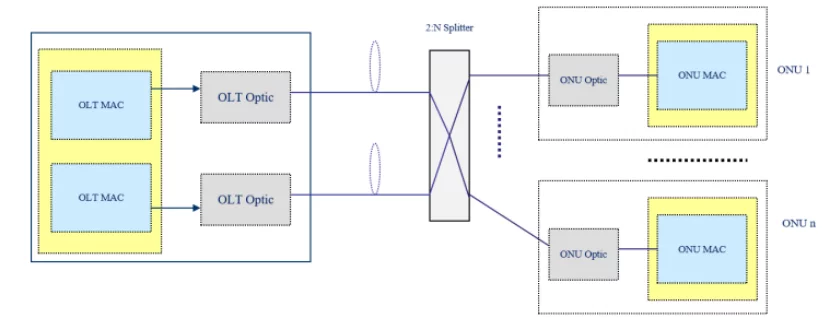
1.4 PON Protection Type C
PON protection type C uses two PON ports on the OLT, and the main standby PON ports are mutually hot backup. ONU uses a PON MAC and different optical modules; a 1×2 optical switch is built in front of the PON port. Two 1: N optical splitters are used to establish two independent and mutually backup optical fiber links between ONU and OLT. The OLT guarantees that the main PON port’s service information can be backed up to the backup PON port simultaneously. Both the ONU and the OLT detect the link status and decide whether to switch according to the link status.
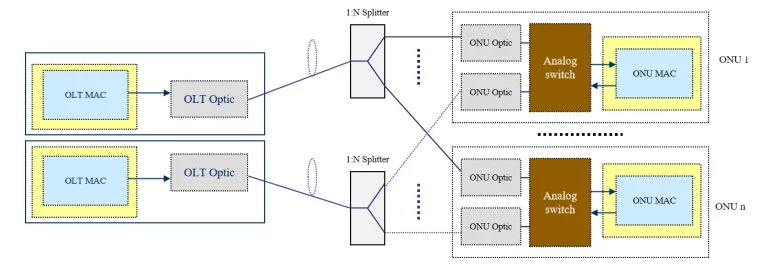
1.5 PON Protection Type D
In PON protection type D, OLT dual PON ports, ONU dual PON ports, backbone fiber, optical splitter, and distribution fiber are all dual redundant. Both the main and standby OLT PON ports are in working condition. OLT guarantees that the active PON port’s service information can be backed up to the backup PON port synchronously. As a result, the backup PON port can maintain the ONU’s service attributes unchanged during the protection switching process.
ONU uses different PON MAC chips and different optical modules. The ONU should ensure that the primary PON port’s service information can be backed up to the backup PON port simultaneously so that the ONU can maintain the local service attributes during the PON port protection switching process. The ONU’s main and backup PON ports are in a working state. The backup PON port does not need to perform the ONU’s initialization configuration and service attribute configuration during the PON port protection switching process. Both ONU and OLT detect the link status and decide whether to switch according to the link status.
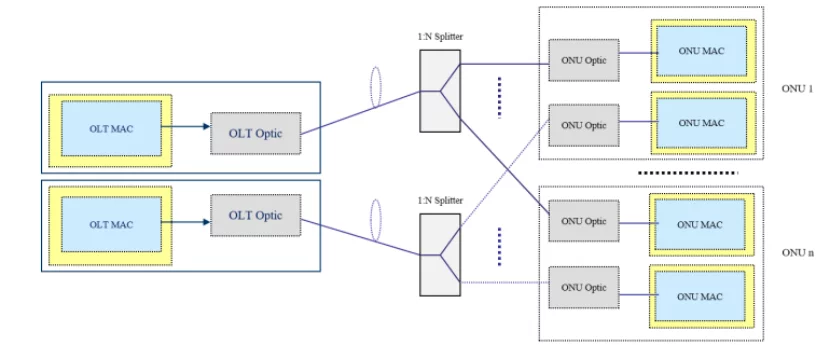
1.6 Choice of 4 Types of PON Protection
The four PON protection types A, B, C, and D protection solutions are introduced above. The OLT’s two PON ports in Type A use 1 PON MAC chip, which is connected to 2 optical modules through a 1×2 switch to realize 2 PON ports’ protection. This type is only applicable to the protection in the same PON board. Although the C and D protection types protect the entire network, making the system the best reliable, the protection cost is too high. Simultaneously, ONU equipment also needs to support the corresponding PON protection function, which only high-end users can afford. So, it is hardly used in actual projects.
Considering the access cost and practicability, Type B protection is more economical and practical. In Type B protection, the OLT’s two PON ports adopt independent PON MAC chips and optical modules to realize the protection of two PON ports, which is suitable for protection between any 2 PON ports of the same OLT.
2.1 PON Protection Group
The PON protection group consists of two access PON ports. The members of the protection group have two roles: work and protect. One is a working port, and the other is a protecting port. Under normal working conditions, the working port carries services. When the optical fiber link in the working port fails, the system automatically switches the working port’s service to the protected port to ensure service transmission.
2.2 Status of Protection Group Member
There are two states of protection group members: active and standby. The port in the active state forwards data and the port in the standby state does not forward data.
2.3 Type of Switching
There are two types of protection group switching: automatic switching triggered by failure and protection switching performed manually. The manual protection switching performed is also called forced switching:
(1) Automatic switching means that the OLT and ONU do not need human intervention to automatically switch the optical fiber link when the switching conditions are met.
(2) Forced switching refers to operating force-switch on the OLT so that optical link switching occurs regardless of whether the designated target member is normal.
To ensure smooth service transition after PON protection switching, the PON protection group’s initial configuration needs to be issued synchronously. The dynamic data during the operation of the protection group also needs to be synchronized. Initial configuration refers to the primary PON port’s static service configuration information in the protection group, such as VLAN, bandwidth, voice configuration, and multicast video service configuration. Dynamic data includes the MAC address learning table, multicast member group information, DHCP binding table, key information.
3.1 Configuration Synchronization
The configuration of the same ONU on the two PON ports in the protection group must be synchronized. The key to configuration synchronization is as follows:
1) All ONUs authenticated on the primary PON port should be synchronized to the standby PON port, allowing the ONU to update its online state structure. The active PON port module should also synchronize the configuration status information with the standby PON port module to avoid repeated configurations and affecting services.
2) Dynamic data synchronization: Dynamic data synchronization refers to synchronizing data from the PON port in the working state to the PON port in the standby state when the data changes. It requires a host CPU for real-time data synchronization.
3.2 Service Recovery
After performing the PON port’s active/standby switchover, the original standby PON port becomes the active port. All PON related configurations and ONU configurations under the PON port should be the same as the original working PON port. After the PON protection switch is completed, all services can be automatically restored when the new working PON port is normally available.
3.3 PON Protection Switching of C-Data OLT Products
With more and more types of services carried by PON networks, to ensure the stability of the services in engineering applications, C-Data combines PON protection in actual engineering, considering the access cost and practicality, and has fully supported PON for protection type B. The user does not need to pay attention to which PON port of the protection group is currently working. All operations are based on the main PON port. When the protection switching is triggered, the standby port state changes to the working state and replace the main PON port to continue to carry services.
As far as we know, the PON protection function implemented by OLT of some manufacturer does not actually implement protection switching but backs up the configuration of the active port to the backup port. The result is that all ONU will be disconnected after the switching, and the service will be lost, which will cause great distress to operation and maintenance personnel. However, our OLT solutions has achieved true protection switching. When the PON port is fully loaded with ONU, ONU can be kept online before and after the switching without service interruption, ensuring network stability safely and quickly.
With the popularization of information technologies such as big data, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and the internet of things, PON technology efficiently supports various industries’ digital development by its technical reliability and practicality and relatively reasonable price advantages. As a professional supplier of network access products, C-Data will provide reliable and stable network deployment to the industries worldwide and apply more PON protection technologies to products. At the same time, it is great for consumers to choose OLT solutions that supports the PON protection of C-Data and jointly promoting the steady development of global digital networks.